

A potentiometer is designed to change a voltage output to the computer, so that when a fuel setting or gas-pedal position is changed, the voltage will change and the computer will read the new voltage and respond accordingly. Input components are divided into electric parts, such as the potentiometer, the variable resistor, the magnetic pickup and the voltage generator.

Inputs and outputs are further divided into analog and digital types of information-analog signals being used with modules that may change continuously (such as oil pressure) and digital signals being used for modules that can simply be on or off (like the headlights or the oil indication light). These components are divided into inputs, such as sensor data about heat or speed, and outputs, or ways in which the body control module computer responds to control the vehicle's electronic functions. While there are many different types of body control modules, they are generally alike, connecting sensors, switches and automatic reactions together in one computer system. A body control module gathers all these separate modules under one system so that they function together instead of separately, a format easier to both manufacture and troubleshoot. There was a module for the air-conditioning, a module for the interior lighting, a module for the door locks, and so forth. When electric devices first began being used in cars and trucks, each device was governed by a separate electric component.
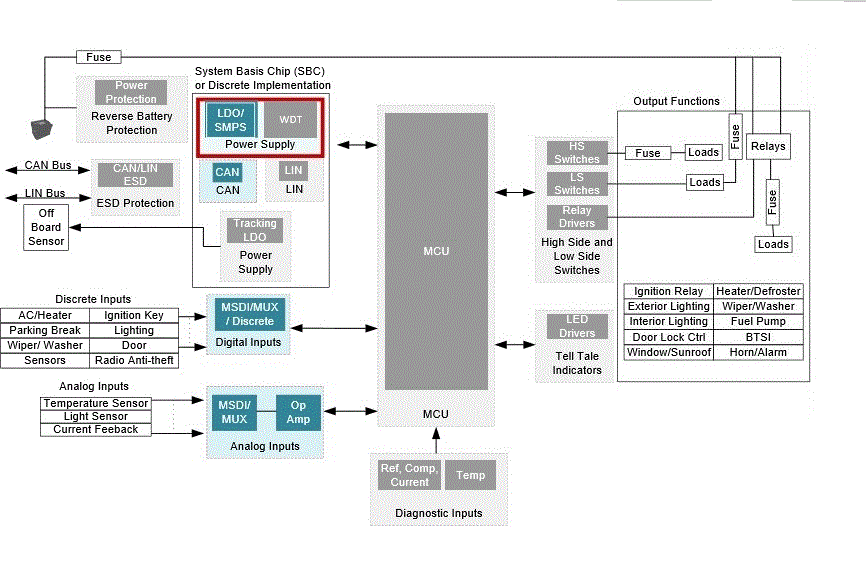
A body control module is a computer component in an automobile that checks, regulates and operates electronic devices throughout the car.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
